
If you're like me, you find it stressful and even a little embarrassing when your car takes a long time to start in the morning or after getting off work.
But why does my car take so long to start?
A vehicle taking a long time to start is most likely caused by a problem with the fuel system, such as a bad fuel pump, the charging system, such as a faulty battery, or the ignition system, such as fault ignition coils.
Other problems such as vacuum leaks, faulty sensors, or malfunctioning anti-theft devices can also cause hard starting.
Below are some steps you can take to troubleshoot and hone in on the system and part causing the problem.
 Frustrated because car won't start
Frustrated because car won't start
Diagnosing Using an OBDII Scanning Tool
First off, I highly recommend buying an OBDII scanner. An OBDII scanner will detect trouble codes that your car's ECU (electronic control unit) returns out.
An OBD2 scanner is compatible with all makes and models post-1996 sold in the USA.
Amazon has a multitude of OBD2 scanners at affordable prices like this one here (paid link).
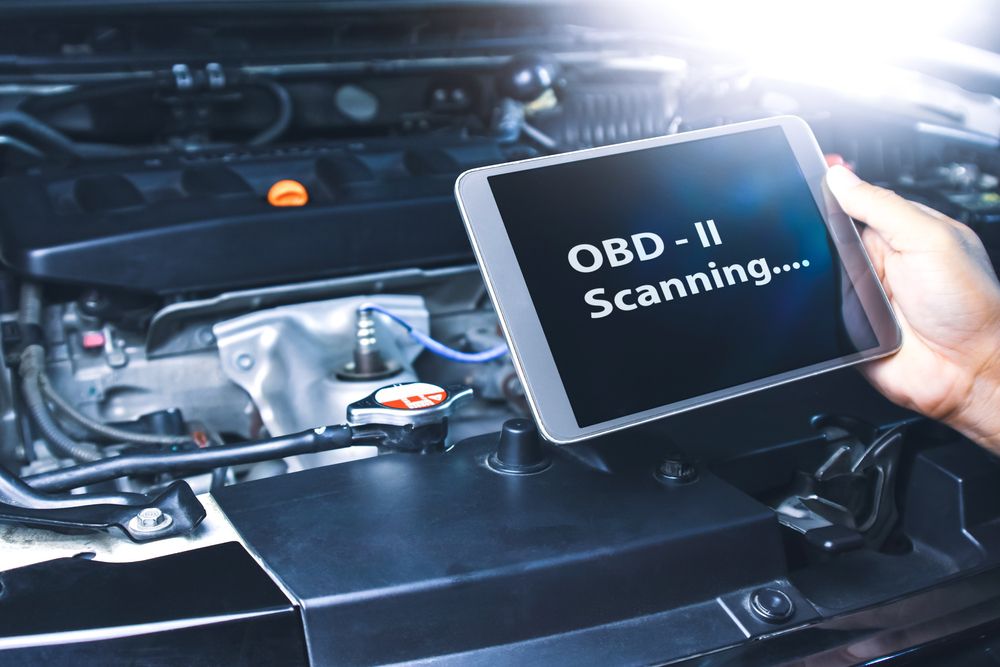 Using an OBD2 scanner to get trouble codes
Using an OBD2 scanner to get trouble codes
Cheap reliable scanners are available for around $20.
They plug into your car's OBDII port and then connect to an app on your phone via Bluetooth.
There are scanners compatible with IOS and/or Android.
Codes returned will often point directly to the charging, fuel, or ignition systems, making troubleshooting far more straightforward, less time-consuming, and cheaper!
Whether or not you have a scanner, you'll want to read through the rest of the article in its entirety to get familiar with the car's systems and how they could be causing your car to take a long time to start.
Charging System
First off, we will have a look at the vehicle's charging system.
 Mechanic charging a car battery
Mechanic charging a car battery
The charging system consists of:
The Battery
- Supplies energy to the starter, which cranks the engine over to start it
- Delivers smooth electricity to electrical power components in the car
As a battery ages, it loses its effectiveness as the chemicals get depleted.
Eventually, as the battery wears out, it will no longer be able to hold a charge large enough to start the car.
A poorly charged or worn-out battery can be why your car takes a long time to start.
The battery will not have the juice to crank the starter fast enough to develop the required momentum to start the engine.
Suppose a battery is worn or depleted. It is important to troubleshoot why! Is it just because it's old? Or is it because a faulty alternator is not charging it properly?
Battery Troubleshooting
A simple way to check the battery is to turn the key over one click until your dash lights up, but the starter doesn't engage, and the car stays off.
Read the voltage gauge, and it should read about 12 Volts. If it reads less, it means your battery is weak.
Then turn the key one more click and start the engine. The voltage meter should now read 14 Volts. If it reads less, it's a good indication that your alternator and or battery are failing.
If you can't start the car, have someone jump-start it and let it run.
After it runs for a while, turn the car off, then try to restart it.
It points to a bad battery if the car doesn't restart as the alternator is providing a charge while the car is running, but the battery is not holding that charge.
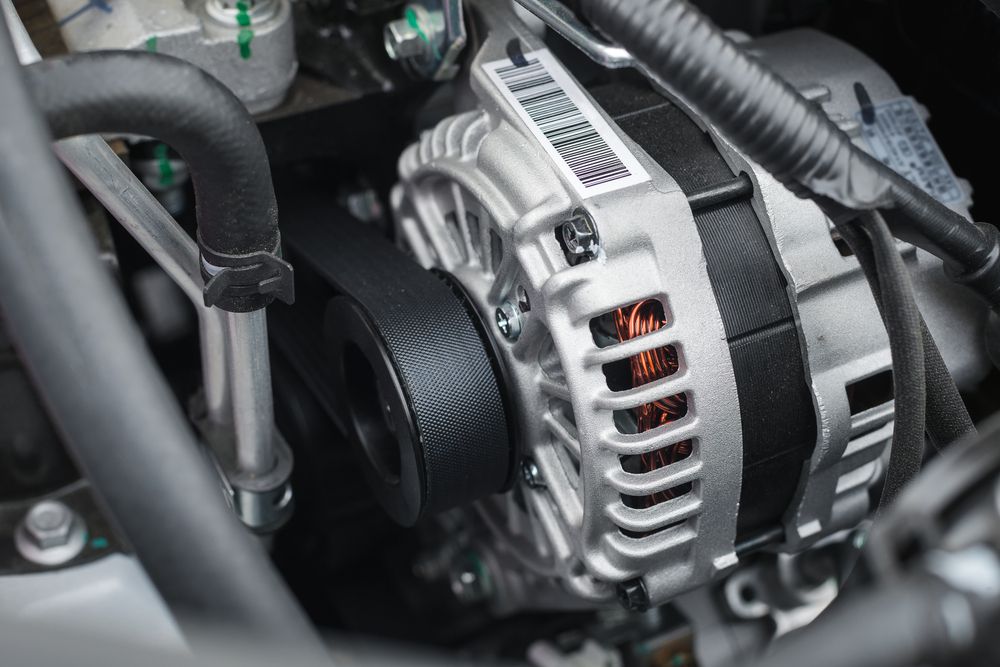 Altenator
Altenator
Alternator
The Alternator keeps the car's battery charged works with the battery to deliver electricity to the car's electrical components.
Bad Serpentine Belt
A bad or worn-out serpentine belt may cause the belt that drives the alternator to slip, leading to the alternator not spinning enough to fully charge the battery.
Check the belt for cracks or listen for belt squeal at the motor.
Bad Diodes
Bad diodes are a common cause of hard-starting.
The alternator's diodes convert the alternator's AC to DC to charge the battery.
If one or two diodes fail, you may still have enough power to charge the battery, but the battery will not get fully charged once a few more fail.
Worn-out brushes can cause a low charging situation.
Brushes provide a contact from the car's battery to the alternator's coil to control the alternator's voltage output.
A foul smell like burning rubber or hot wires can mean the alternator is overheating, and it's time to replace it.
Starter
An electric motor provides the initial cranks to the car's engine to start it.
Troubleshooting A Bad Starter
First, ensure there is voltage going to the starter! If no voltage reaches the starter, fix that first, as the starter is probably not the problem!
If you are sure there is voltage going to the starter, the following symptoms could be an indication of a bad starter:
- No response when turning the ignition
- The starter makes a clunking noise but does not engage with the motor
- The starter spins but does not engage with the motor
- If you turn the key and the engine turns over, it's not a starter issue.
A faulty starter could have multiple causes:
- Faulty electrical connection: Inside the starter, there are electrical contacts that, when engaged, power the starter. Over time these contacts can wear out and provide less power to start the motor. Eventually, you won't have enough power to turn the engine, at which point you will need a new starter.
- Faulty solenoid
- Electrical motor damaged, perhaps from leaking oil
- Gear pinion or freewheel damaged
The Wiring and Fasteners
The wiring connects the various components of the car's electrical system
Look for melted wirings, disconnected connections, shorts, corrosion, etc.
Lousy wiring to the starter can cause a vehicle to take a long time to start or start inconsistently.
Two wires go to the starter:
- One thick line from the battery supplies power to the starter to crank the motor over.
- A second smaller wire from the ignition switch in the car detects when the key has been turned to activate the starter and crank the motor.
If one of these wires is damaged or if there is a poor connection in the circuit, it can cause the vehicle to take a long time to start.
Bad wires or corroded terminals can prevent the battery from charging properly.
Inspect the wires for cracks, disconnect the fasteners from the battery, and clean the terminals with a wire brush.
The Fuel System
If you have confirmed that you have a good battery, alternator, and starter, the fuel system is the next place to look.
The fuel system consists of a pump, filter, regulator, and injectors.
The pump pumps fuel through the filter and injectors and finally into the engine's combustion chamber.
Troubleshooting The Fuel System
To diagnose the fuel system, you can use a fuel line pressure gauge. Most fuel systems run between 35 and 45 psi.
With the gauge tied into the fuel line, the ignition is turned to the first position without turning the car on. Pressure should build instantly.
You turn the key back to the off position and monitor the pressure over 10 minutes, ensuring that pressure doesn't bleed off quickly. If pressure leaks off quickly, that could signify a faulty regulator or a faulty check valve in the fuel pump.
Low fuel pressure can cause hard starts because an insufficient amount of fuel is reaching the engine for combustion to occur.
This is called running lean. A number of things can cause low fuel pressure:
- A clogged fuel filter - the fuel filter is located between the pump and the engine.
- A plugged-up fuel filter can prevent the necessary amount of fuel from getting to the injectors.
- Faulty Fuel Regulator - A broken diaphragm spring in the fuel regulator can cause low fuel pressure.
Diagnosing a Faulty Fuel Pump
Fuel pump failure is quite common and they are pretty easy to troublshoot. Just follow these steps:
- Check to see if you can hear the fuel pump running.
- Turn the key in the ignition one click to the ACC setting to light up the dash but not start the motor.
- Listen near the gas cap and see if you can hear a buzzing sound from the fuel pump.
- Next step if you don't hear the fuel pump running is to go under the hood and check the fuse for the fuel pump.
- There can also be a fuel pump relay in the fuse box. Have somebody turn the key on and see if you can hear the relay click.
- The next step is to hook up a fuel pressure gauge to the fuel rail and see what pressure we have that the fuel pump is producing. Turn on the key without starting the motor and monitor the pressure gauge. Healthy pressure is around 45-60psi. If you don't see any pressure or the pressure bleeds off rapidly, the problem could be a faulty fuel pump pressure.
- If you see pressure and then it bleeds off, there could be another leak in the system that you want to look for before you dig up the fuel pump from the gas tank.
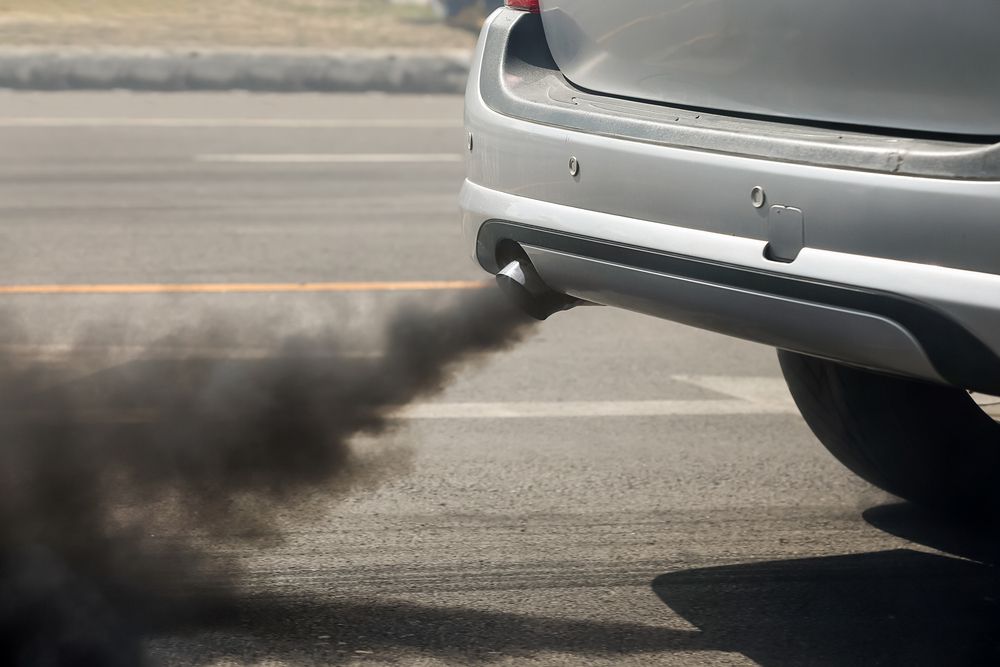 Black car exhaust
Black car exhaust
Faulty Fuel Pressure Regulator
The fuel pressure regulator is the component responsible for regulating the pressure of the fuel pumped to the injectors.
Many regulators are vacuum powered, and some are electronically controlled.
If your car takes a long time to start, plus one of the following symptoms is occurring, you will want to dig in deeper and investigate your fuel pressure regulator.
There are a few common symptoms of a faulty regulator:
- Black smoke coming from the exhaust: Black smoke coming from the exhaust almost certainly points to a bad fuel regulator. Black smoke coming from the exhaust is caused by too much fuel entering the combustion chamber, or in other words, the engine is running rich.
- Gasoline dripping out of your exhaust pipe: Gasoline dripping out the exhaust pipe can be caused by a leaky fuel regulator leaking fuel through its vacuum line through to the intake manifold, causing the engine to run rich.
- Strong gas smell: Again a strong gas smell means the engine is running rich and would most likely be caused by a faulty fuel pressure regulator.
Helpful Hint: A quick diagnostic technique is to disconnect the vacuum hose from the end of the fuel regulator and see if any fuel leaks out of the regulator.
Leaking fuel points to a diaphragm leak, and the regulator will need to be replaced.
Dead Or Clogged Injectors
To diagnose an injector first, you need a mechanic stethoscope, or a long thin rubber hose will work. Then do the following steps:
- While the car idles, place the stethoscope or hose up to each injector and listen for the injector tick.
- If you don't hear a tic noise, you may have a faulty injector, making a vehicle difficult to start.
- You may also get a check engine light with misfire codes on your OBD2 scanner.
To check for a clogged injector, you need an injector tester. The tester simulates the injector system allowing you to diagnose each injector individually to find the clogged injector. You can then clean or replace the injector.
Ignition System
A vehicle's ignition system is often the reason why a vehicle takes a long time to start.
If your engine is flashing a check engine, check that first! It may give you a misfire code pinpointing the exact cylinder that is misfiring, saving you a ton of time troubleshooting!
Ignition systems in modern vehicles can be complicated and vary between vehicles, but a commonality is the ignition coils and spark plugs.
Fouled Spark Plugs
A fouled spark plug has a harder time igniting the fuel in the engine, which can cause your vehicle to take a long time to start.
You can check if you have spark with a spark light test tool available at all automotive parts stores.
Crankshaft/Camshaft Sensors
Through the crankshaft and camshaft position sensors, modern cars use a computer to detect when the ignition system should deliver spark to the combustion chamber.
They will generally throw a code to the scanner if they fail.
Vacuum Leaks
A vacuum leak can lead to hard starts and/or rough idles.
To check for vacuum leaks, you can first visually inspect any cracked or disconnected hoses.
You can also use a smoke tool or carb cleaner to try for changes in idle.
Air Intake Tube
Air Intake Tube can be torn or cracked.
This can lead to additional air entering the engine without the requisite increase in fuel, leading to long crank times at startup.
Mass Air Flow Sensor
The car's MAF (mass air flow Sensor) can cause a mixture issue due to contamination.
You can often fix this by cleaning the MAF sensor with a can of MAF cleaner.
You can even try temporarily unplugging the sensor to see if the problem goes away or improves.
Anti-Theft System
A Problem with the car's anti-theft system could be why the car won't start.
Some vehicles have an anti-theft system that consists of a chip in the key and a receiver inside the vehicle.
The key communicates with the receiver to let it know that it is the right key for the vehicle to start.
Why Does My Car Take Longer To Start When It's Cold?
A car can be difficult to start when cold for a few reasons.
One reason is that the car's computers need time to calibrate themselves.
When a car's engine is warmed up and running consistently, the computer knows exactly when to provide fuel and spark. During startup, the computer may need a few moments to calibrate itself and figure out the proper spark and fuel timing.
The most obvious thing to do first is to see if a check engine light is on.
If so, you can use an OBD2 code reader to check your codes.
Google is your friend, and you can google your code to find out if it is related to difficult starts and what components may be causing the problem.
Conclusion
If your car takes a long time to start, it's essential to find out why before it leads to more significant problems and maybe leaves you stranded.
An OBDII scanner tool is probably worth the investment as it can save you time and money in diagnosis.
The are many possible causes why a vehicle is taking a long time to start, including problems with the fuel, charging, and/or ignition systems.
Luckily, it is possible to narrow down the cause with a bit of work.
However, it may be better to avoid the headache and just take your vehicle to a licensed mechanic for a professional diagnosis.