
Viscosity is the measurement of the resistance to a flow of a fluid. Motor oil viscosity numbers are based on a scale created by the American Petroleum Institute.
The recommended oil viscosity for your vehicle will depend on the engine type in your vehicle and the temperature outside. For example, for older engines, a manufacturer often recommends a lower viscosity oil for colder climates. Therefore, using the engine oil recommended in your vehicle's owner's manual is important.
Keep reading if you want to learn more about the differences in thickness between different types of motor oil. We'll be discussing the thinnest engine oil, engine oil viscosity, engine oil density, and other relevant topics.
 An engine oils viscosity is displayed prominantly on its container.
An engine oils viscosity is displayed prominantly on its container.
Which Engine Oil Is Thickest?
The thickest engine oil commonly available is 40W70 motor oil which has a 40 cold temperature cold start viscosity and a 70 operating temperature viscosity.
You typically won't require an engine oil this thick for most modern cars.
However, if you have an old or antique vehicle, the engine may need extra-thick oil so that it doesn't burn off too quickly, as these cars can burn a lot of oil.
In short, engine oils with the highest viscosity ratings ("W" rating) will be the thickest oil options.
What Does Engine Oil Viscosity Mean?
Viscosity is the most critical factor when considering engine oil's thickness.
Motor oil thickness is determined based on the operational viscosity (thickness at engine operating temperature) and the winter rating (W).
The thickest motor oils have the highest operational viscosity (70 at most) and the highest winter rating (40W at most).
Oils with high operational viscosities run best at hot temperatures, whereas the ones with lower W ratings perform better in the cold.
 Viscosity measures a liquids resistance to flow.
Viscosity measures a liquids resistance to flow.
Viscosity is a thickness measurement of a liquid's resistance to deformation at a specific rate, or in other words its restistance to flow.
Whether or not an engine oil product has a winter rating, it will always have an operational viscosity rating.
The benefits of a low viscosity oil are that it has better fuel economy and flows better in cold weather.
A higher viscosity oil maintains a higher level of lubrication at high temperatures by providing a thicker layer between moving parts in the engine.
The typical units that measure viscosity include the following:
- PI (poiseiulle)
- cST (centistokes)
- 10-6 reyns (lb s/in2)
Keep in mind that engine oil viscosity isn't going to remain constant at all times.
It inevitably varies depending on how hot or cold your engine is, the surrounding weather conditions, and the conditions you're putting your vehicle through.
Engine Oil Thickness Chart
Consider the following thick engine oils' comparative densities (in kg/m3) and viscosity (in centistokes) levels.
Note that density measurements are based on engine oil temperatures of 60 degrees Fahrenheit, and viscosity measurements are based on engine oil temperatures between 100-104 degrees Fahrenheit.
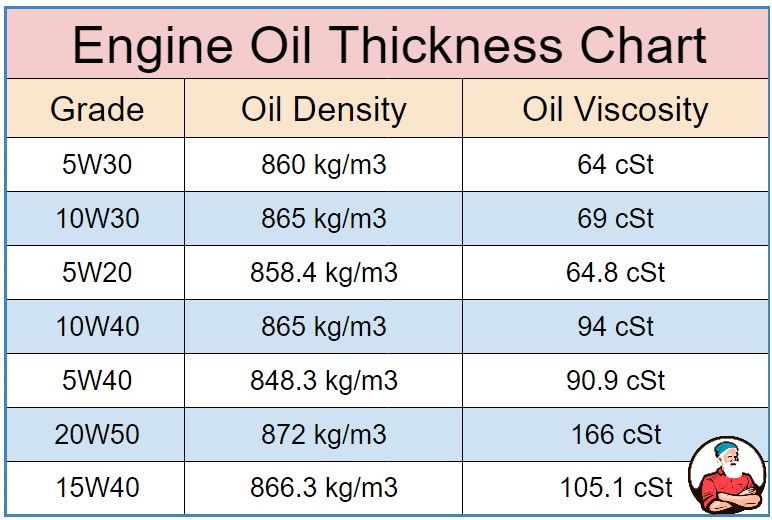 Engine Oil Thickness Chart
Engine Oil Thickness Chart
How To Tell The Thickness Of Motor Oil?
It's fairly simple to figure out how thick oil is, as it's rated based on viscosity.
The rating is a number alongside a "W," followed by a dash and another number.
For example, consider "15W-40" rated engine oil: the number to the right (40) is the viscosity when the engine is warm and running.
You just need the number to the right of the dash to determine thickness (higher means thicker, lower means thinner).
And the number to the left (15) is the "Winter" or "W" rating.
It rates engine performance at colder temperatures.
Lower W numbers signify better performance than higher numbers do.
Which Oil Is Thicker, 5w30 Or 10w30?
Because 5W-30 oil and 10W-30 oil have the same viscosity rating of 30, we have to look to the number before the "W" to determine their comparative thicknesses.
5W-30 engine oil has a 5 winter rating, and 10W-30 engine oil has a 10 winter rating.
Thus, the 10W-30 engine oil is ultimately the thicker option when your engine is turned off at colder temperatures.
 5W30 engine oil container
5W30 engine oil container
Which Oil Is Thicker, 5w20 Or 5w30?
5W20 and 5W30 engine oils differ in that 5W-30 engine oil is thicker (and higher in viscosity) at engine running temperatures, but they have the same winter rating of 5 (5W).
This means they will run at the same thickness at cold start-up temperatures.
So, overall, you have a thicker engine oil when you choose 5W-30.
Which Motor Oil Is Thicker, 10w30 Or 10w40?
Next, let's compare motor oils of the following ratings: 10W-30 vs. 10W-40.
10W-40 engine oil has a higher viscosity by an amount of 10 when compared to 10W-30 engine oil.
Therefore, 10W-40 engine oil is thicker at hotter, running engine temperatures and won't flow as quickly.
Otherwise, they have the same winter (W) rating of 10, meaning they will run at the same thickness at start up in cold temperatures.
Which Is Thicker, 5w30 Or 5w40?
Both 5W-30 and 5W-40 engine oil will flow better at start-up in colder (winter) temperatures.
They have the same W rating, meaning they don't compare in that respect.
But these two oils flow differently at operational engine temperatures (when the engine is running).
Specifically, 5W-40 engine oil is thicker than 5W-30 engine oil and will flow at a slightly lower rate (because 40 is greater than 30).
Is 10w40 Thicker Than 5w30?
10w40 is a thicker oil than 5w30 at both operating temperature (a viscosity grade of 40 is greater than 30) and in cold weather start-up conditions (a viscosity grade of 10 is greater than 5).
Is 10w30 Thicker Than 5w20?
10w30 is a thicker oil than 5w20 at both operating temperature (a viscosity grade of 30 is greater than 20) and in cold weather start-up conditions (a viscosity grade of 10 is greater than 5).
Is 20w50 Thicker Than 10w40?
Both 20W50 motor oil and 10W40 motor oil are relatively thick oil options, but 20W50 is a more viscous oil than 10W40 at both operating temperature (a viscosity grade of 50 is greater than 40) and in cold weather start-up conditions (a viscosity grade of 20 is greater than 10).
Is 20w50 Thicker Than 10w30?
20w50 is a thicker oil than 10w30 at both operating temperature (a viscosity grade of 50 is greater than 30) and in cold weather start-up conditions (a viscosity grade of 20 is greater than 10).
Is 15w40 Thicker Than 10w30?
15w40 is a thicker oil than 10w30 at both operating temperature (a viscosity grade of 40 is greater than 30) and in cold weather start-up conditions (a viscosity grade of 15 is greater than 10).
What's Thicker, 5w Or 10w?
When we compare the "W" rating alone for motor oil grades, we compare their relative viscosity at cold temperatures before the engine started.
Therefore, 10W rated oil is thicker, but only at cold temperatures.
You would also have to compare their operational viscosities to know which is thicker at driving temperatures.
Which Oil Is Thicker SAE 30 Or 40?
When dealing with SAE engine oils, only one rating number is involved; we have to consider that these are single-grade oils.
This means that they are only rated for their operational viscosity (a.k.a. How thick/thin are they when they get hot and the car is running?)
Knowing this, we can determine that SAE 40 engine oil is thicker than SAE 30 engine oil.
Which Motor Oil Is The Thinnest?
Now that we're aware of the comparative viscosities of engine oils, we can see that the thinnest engine oil will have the lowest operational viscosity.
SAE 16 (single-grade motor oil) is the thinnest oil option regarding operational viscosity.
But if we're considering multi-grade motor oils, a 0W-16 is the overall thinnest option you can find for vehicles.
0W-16 engine oil means you have the best performance at cold temperatures and the lowest viscosity rating at operational engine temperatures.
Conclusion
The thickest motor oil available is 40W70 motor oil. 40W70 motor oil has a 40 winter cold start grade viscosity and a 70 operating temperature viscosity.
Until the last ten years, vehicles required a higher viscosity oil in the summer and lower viscosity in the winter to achieve proper lubrication.
Nowadays, engines are manufactured with tighter tolerances and achieve good oil pressure with lower viscosity oils. Lighter oils have the added benefit of better fuel economy.
References
https://www.substech.com
https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com
https://en.wikipedia.org
https://shop.sclubricants.com
https://www.aqua-calc.com
https://micdot.com
https://www.chevronmarineproducts.com
https://www.atlanticoil.com
https://www.firestonecompleteautocare.com