
The various systems in virtually all modern vehicles are controlled by computers (ECU).
The vehicle's computer system receives information from sensors throughout the vehicle. It uses this information to ensure the vehicle runs optimally.
If the oxygen sensor, crankshaft position sensor, mass air flow sensor, camshaft sensor, knock sensor, or throttle position sensor is faulty, your engine may not start. The sensor will have to be replaced before you can start your car.
If you're having trouble starting your vehicle, you may have a faulty sensor. Keep reading to learn when a bad sensor causes a car not to start and how to handle the problem.
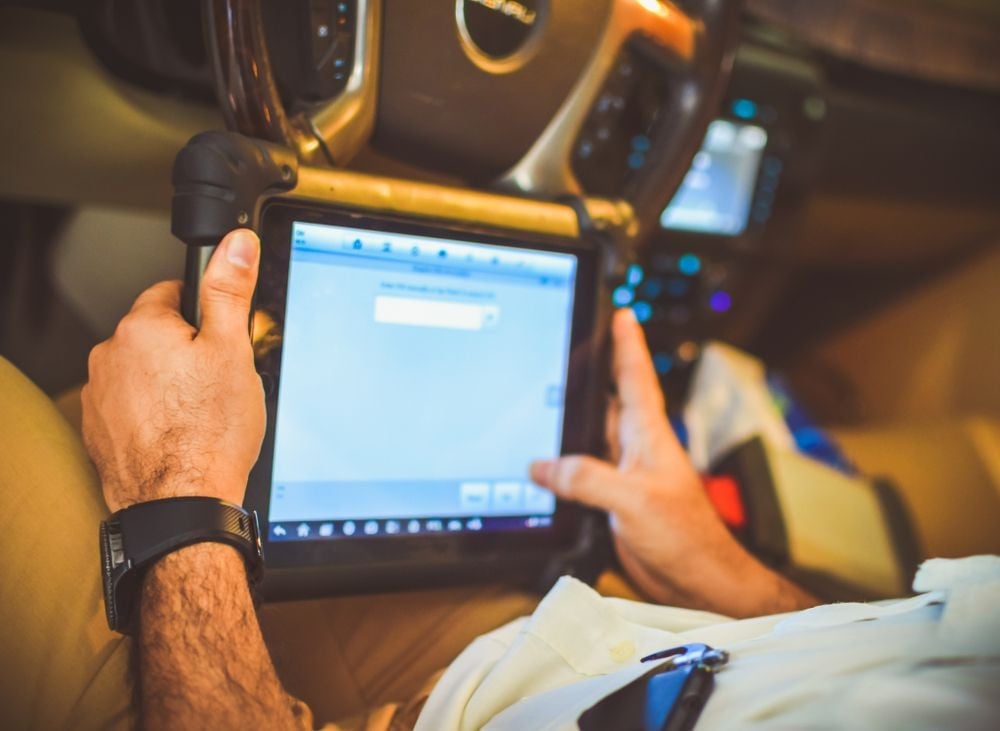
 Mechanic pulling sensor trouble codes
Mechanic pulling sensor trouble codes
1. O2 Sensor
An O2 sensor is a device that monitors the oxygen content of a car's exhaust.
The sensor is used to help the car's computer adjust the air/fuel mixture to optimize engine performance and efficiency.
If the engine doesn't maintain the proper balance of air to fuel, it can accelerate slowly and burn more fuel than necessary.
Can an O2 Sensor Cause My Car To Not Start?
Most likely, it is not the O2 sensor that is preventing your car from starting.
Compared to other types of sensors, O2 sensors do not activate as soon as you start up the car. Instead, they remain inactive until they reach around 650 degrees Fahrenheit.
It would be inefficient for the sensor to activate before that point because it measures oxygen levels in the exhaust once the engine has warmed up and stabilized.
However, a faulty O2 sensor can cause your engine to stall after it first starts.
 Oxygen Sensor
Oxygen Sensor
What Does an Oxygen Sensor Do to a Car?
The oxygen sensor is responsible for detecting the amount of oxygen released from your car's engine.
This information is then sent to the ECU and used to determine the perfect balance of oxygen and fuel for efficient combustion.
If the engine intakes too much oxygen, it's said to be burning lean, leading to a loss of power and decreased fuel economy.
On the other hand, if there's not enough oxygen, the engine is said to be running rich, leading to fouled spark plugs and an increased risk of engine damage.
How Much is an O2 Sensor?
The cost of an O2 sensor can vary depending on the make and model of your car. However, on average, you can expect to pay between $200 and $500 for a new O2 sensor.
What Happens When an O2 Sensor Goes Out?
When an O2 sensor goes out, it cannot correctly gauge the amount of oxygen in your vehicle's exhaust.
It may give a false read that affects the balance of fuel to air within the combustion chamber.
This will cause your engine to lose performance and burn through fuel at a faster rate. Your engine may even stall.
If you think your O2 sensor may be going bad, you can check a few ways.
One way is to use a code reader to check for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
If the code reader detects a P0131, P0132, P0133, or P0134 code, the O2 sensor is not functioning correctly.
Another way to tell if the O2 sensor is going bad is to monitor the oxygen sensor's voltage with a multimeter.
If the voltage is fluctuating erratically, it's a sign that the O2 sensor is going bad.
You can also check the O2 sensor by starting the engine and letting it idle.
If the engine is idling smoothly, it's a good sign that the O2 sensor is working correctly.
However, if the engine is idling roughly, it's a sign that the O2 sensor is going bad.
2. Crankshaft Position Sensor
The crankshaft position sensor consists of a magnet and a sensor that is attached to the crankshaft.
As the crankshaft rotates, the magnet spins past the sensor and produces a signal that is sent to the ECU.
The ECU uses this signal to determine the crankshaft's position and to control the timing of ignition and fuel injection.
Without a properly functioning crankshaft position sensor, your engine will not be able to correctly time fuel injection, and your engine will not perform well.
There are ways to bypass a malfunctioning crankshaft position sensor so you can drive your vehicle to a mechanic.
 Crankshaft position sensor
Crankshaft position sensor
Will the Crankshaft Sensor Keep the Car from Starting?
Since the crankshaft position sensor plays a vital role in the ignition system, there's a high likelihood that your engine will not start if the sensor has gone bad.
If the sensor is only starting to degrade, your engine may start, but you'll notice trouble before it finally ignites.
How Do You Diagnose a Bad Crankshaft Sensor?
If you have a crankshaft sensor that has gone bad, you may notice one or more of the following symptoms:
The engine will not start
The engine will misfire
The engine will stall
The engine will have a hard time starting
The check engine light will come on
What are the Symptoms of a Failing Crankshaft Position Sensor?
The most obvious symptom of a failing crankshaft position sensor is if your engine repeatedly misfires.
When the sensor goes bad, your ECU won't get the proper information needed to control timing, so the cylinders will repeatedly misfire, eventually causing your engine to stall.
How Do You Check a Crankshaft Position Sensor?
If you notice any of these symptoms, it's a good idea to take your car to a mechanic and have them check the crankshaft sensor with a code reader.
If the code reader detects a P0335, P0336, P0337, or P0338 code, the crankshaft sensor is not functioning correctly.
Another way to tell if the crankshaft sensor is going bad is to check the sensor's voltage with a multimeter.
If the sensor's voltage fluctuates erratically, it's a sign that the crankshaft sensor is going bad.
3. Mass Air Flow Sensor
A mass air flow sensor is important in a vehicle's engine management system.
It is used to measure the amount of airflow into the engine.
The sensor is usually located in the air intake system and sends information to the ECU to calculate the amount of fuel to be injected into the engine.
Much like the O2 sensor, it is also used to monitor the engine's air/fuel mixture.
 mass air flow sensor (MAF)
mass air flow sensor (MAF)
Can a Mass Air Flow Sensor Cause a Car to Not Start?
Depending on how poorly your mass air flow sensor is working, it can cause your vehicle not to start.
Leading up to a complete non-startup, you'll notice your vehicle start to lose power on acceleration and other drivability problems.
How Can You Tell if a mass air flow Sensor is Bad?
A bad mass air flow sensor can cause several problems with a car.
The most common symptom is a decrease in fuel efficiency, but a bad mass air flow sensor can cause an engine to stall frequently, run roughly, or fail to start.
How To Test A mass air flow Sensor?
To properly test the sensor, first find its location on your vehicle. The location will vary depending on the make and model of your car, but it is usually located near the air filter box.
Start the engine and let it idle for a few minutes. Then, turn the engine off and disconnect the mass air flow sensor's electrical connector.
Test the sensor for continuity between the two terminals on the electrical connector using a multimeter. There should be continuity. If there is not, the sensor is defective and needs to be replaced.
4. Camshaft Sensor
Camshaft sensors are used by the engine control unit (ECU) to synchronize the ignition timing and fuel injection with the position of the pistons.
This ensures that each cylinder fires precisely at the right time, improving combustion efficiency and preventing engine knock.
The ECU uses signals from both camshaft sensors to determine when each piston is at top dead center (TDC).
It sends a signal to the ignition coil, telling it when to fire spark plugs and inject fuel into each cylinder for optimal efficiency.
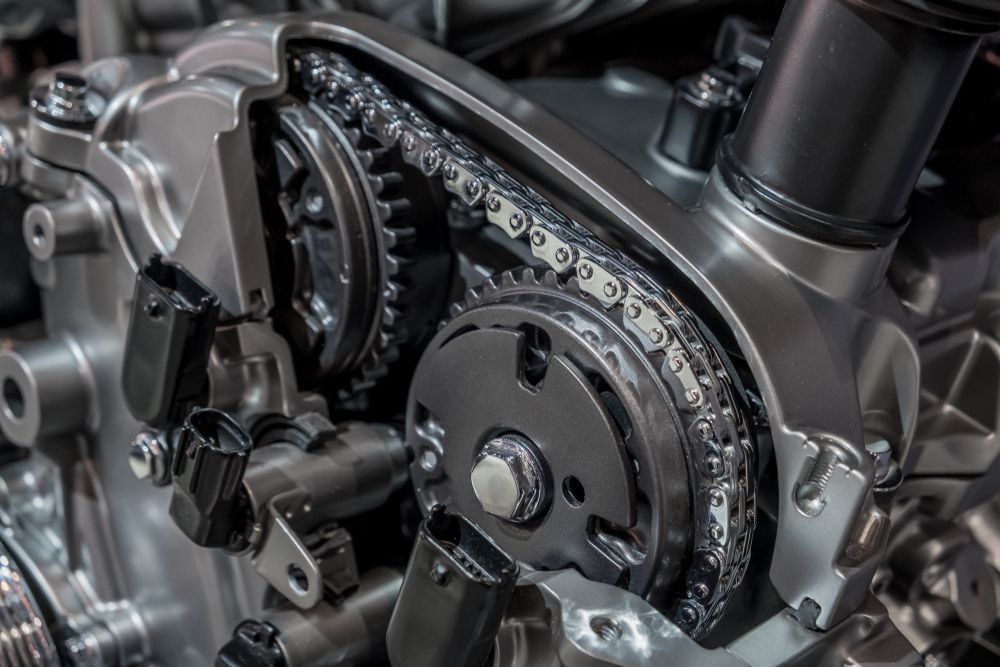 Camshaft position sensor
Camshaft position sensor
Will the Camshaft Sensor Cause a No-Start?
If the camshaft sensor is not working correctly, the engine will not start. This is because the ECU needs information from both camshaft sensors to synchronize the ignition timing and fuel injection.
If one of the sensors is not working, the ECU cannot correctly determine when each piston is at TDC.
This will cause a misfire, which can prevent the engine from starting.
If you're worried that a faulty camshaft sensor is preventing your vehicle from starting, there are several ways to test the parts:
Check for power and ground at the sensor connector using a voltmeter. The power wire should have battery voltage ( typically 12 volts). The ground wire should have 0 volts.
Use an oscilloscope to check for pulses on the signal wire while cranking or running the engine. There should be one pulse per revolution of the crankshaft or two pulses per revolution of the camshaft (depending on which type of sensor you have).
If neither of these methods works, you can try replacing the sensor with a new one.
Where is the Cam Sensor Located?
Most camshaft sensors are near the engine's top, behind the timing belt cover.
They are usually mounted on the cylinder head or intake manifold.
The sensor consists of a magnet and a Hall effect sensor, which produces an electrical signal when exposed to a magnetic field.
As the camshaft rotates, the magnet passes by the sensor, producing pulses of electrical current.
The ECU uses these pulses to determine the position of each piston in its cylinders.
How many Camshaft Sensors are in a Car?
Most engines have two camshaft sensors: one for each camshaft.
Some engines, such as those with VVT (variable valve timing), may have additional sensors.
5. Knock Sensor
A knock sensor is a sensor that is mounted on an engine and designed to detect knocking.
Knocking is a type of engine noise that happens when the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders is detonating too early, which can cause damage to the engine.
The knock sensor sends a signal to the engine control unit (ECU) when it detects knocking, and the ECU then adjusts the ignition timing to prevent further damage.
However, if the sensor malfunctions, the engine will not adjust and could break down.
What is a Knock Sensor?
A knock sensor is usually mounted on the engine block near the cylinder head.
It consists of a piezoelectric crystal that produces a voltage when it is vibrated.
When the sensor detects a strong vibration emanating from the engine, it sends a signal to the ECU.
The ECU then adjusts the ignition timing to prevent the air-fuel mixture from combusting before it should.
As with any part, knock sensors can degrade over time and eventually malfunction.
For example, your vehicle's knock sensors may fail due to physical damage, such as a sensor crack, or electrical issues, such as a short circuit.
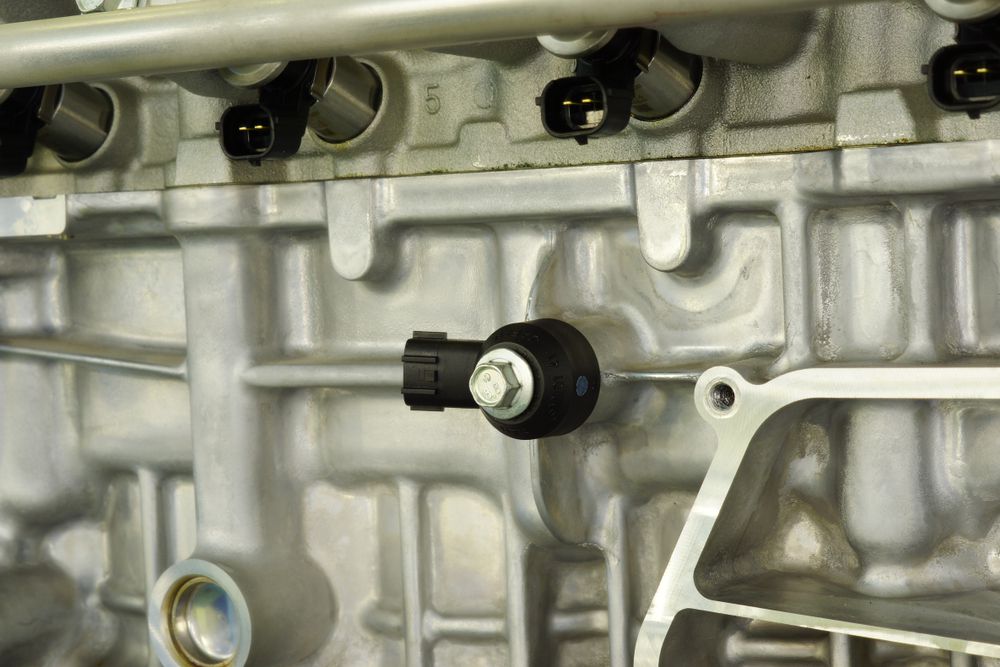 Knock sensor
Knock sensor
Can I Drive With a Faulty Knock Sensor?
A broken knock sensor will not cause your engine to stop working, but it will prevent the ECU from adjusting the ignition timing.
This can lead to engine damage over time, so driving with a faulty knock sensor is not advisable.
If your check engine light is on, you should take your vehicle to a mechanic and have it diagnosed.
They will be able to tell you if your knock sensor is the issue and replace it if necessary.
Additionally, you'll notice the following symptoms:
Reduced fuel economy
Poor engine performance
Increased engine noise
Misfire and slow acceleration
If you detect any problems, take your vehicle to a mechanic as soon as possible.
How Do You Bypass a Knock Sensor?
If your knock sensor is not working, you can bypass it by disconnecting the sensor and plugging the hole.
This will allow the engine to run without the sensor, but it is not recommended as it can lead to engine damage.
Ideally, it is best to replace the knock sensor if it is not working.
How Do You Fix a Knock Sensor?
If your knock sensor is malfunctioning, you can try cleaning it with a wire brush or replacing it.
If the sensor is physically damaged, you will need to replace it by disconnecting the old sensor and connecting a new one in its place.
You can access the sensor by removing the intake manifold.
Once you have access to the sensor, you can test it and decide whether it's best to switch it to a new one.
6. Throttle Position Sensor
The throttle sensor is a device that measures the position of the throttle. It is typically located on the throttle body and consists of a potentiometer and a sensor.
Signals from the throttle position sensor are sent to the ECU and used to determine the amount of air entering the engine.
What Does a Throttle Position Sensor Do?
The throttle position sensor consists of a potentiometer and a sensor.
The potentiometer measures the position of the throttle, and the sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine.
The throttle is a small valve that allows air to enter the engine. If it's opened too wide, your engine will flood with oxygen and burn too lean.
However, by working together, these two parts can provide information to the ECU about the amount of air mixing with fuel and allow your vehicle to adjust the throttle to regulate combustion better.
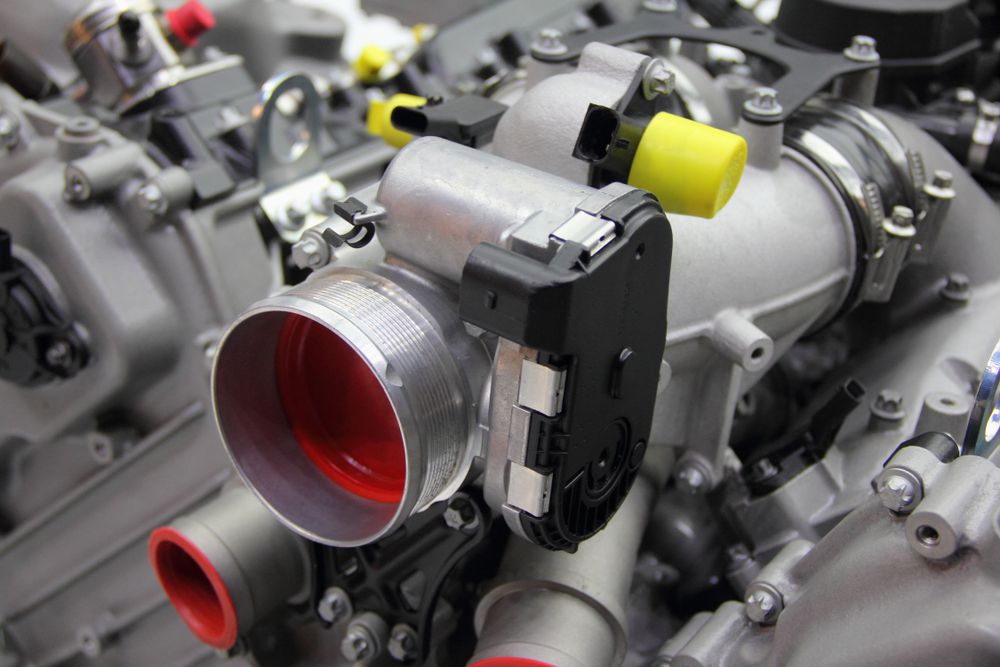 Throttle position sensor
Throttle position sensor
What are the Symptoms of a Bad Throttle Position Sensor?
If your car's throttle position sensor has become faulty, the engine will likely still start, but you'll find that it lacks power and may eventually stall out.
If you notice any of these other symptoms, your throttle position sensor is likely about to fail:
The engine may hesitate or stall when you try to accelerate.
The engine may run rough
The check engine light may come on
The engine may misfire
The engine may experience decreased fuel economy
If you've noticed any of these problems, test your vehicle's throttle position sensor and replace the necessary part.
How to Test the Throttle Position Sensor?
There are a few ways that you can test your throttle position sensor:
Use a multimeter to test the sensor's voltage output. It should give a readout between 0.5 and 4.5 volts. If the sensor is damaged, it may give a false reading or no reading at all.
Check the sensor's resistance with an ohmmeter. A properly functioning sensor should produce between 1.5 and 4.5 ohms of resistance. If not, the sensor has gone bad and should be replaced.
Inspect the sensor for physical damage. Check for cracks, breaks, or any other damage around the wires and connectors.
If your vehicle has issued a check engine light, use a scanner to check for error codes.
Amazon has a multitude of OBD2 scanners at affordable prices like this one here (paid link).
If any of these tests indicate that your throttle position sensor is damaged, we recommend getting it fixed as soon as possible.
How to Replace a Throttle Position Sensor?
Follow these steps to replace a damaged or faulty throttle position sensor:
Start by disconnecting the negative battery terminal to prevent any electrical shorts.
Locate the throttle position sensor. It is typically located on the throttle body.
Remove the old sensor and install the new one in its place.
Reconnect the negative battery terminal.
Start the engine and test the throttle position sensor to ensure it works properly.
If the sensor works correctly, your engine will start and perform with full power.
Other Reasons Your Engine Cranks But Won't Start
Apart from faulty sensors, if your engine cranks but won't start you could have a:
faulty fuel pump - a faulty fuel pump won't provide the necessary fuel pressure to start the vehicle
a broken timing belt or timing chain
dirty or faulty fuel injectors
worn starter motor
Conclusion
A sensor can prevent a car from starting. The first thing to check is whether your check engine light is on and what trouble codes your ECU is returning. Sensors that can prevent your car from starting are the oxygen sensor, crankshaft position sensor, mass air flow sensor, camshaft sensor, knock sensor or throttle position sensor.